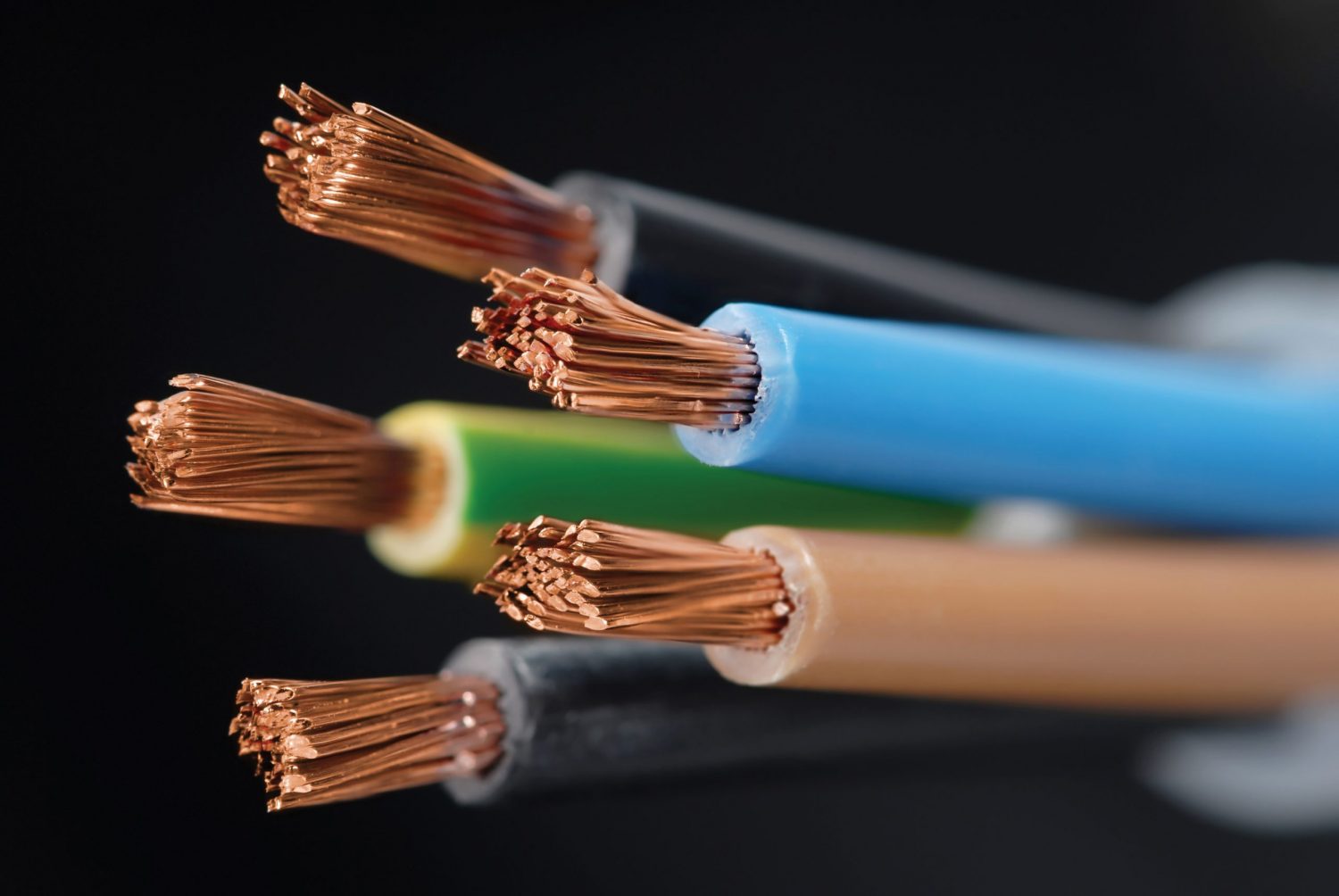
As we have repeatedly stated in the articles we publish on the blog Ricablea cable, especially if Hi-Fi, is composed of many parts. Conductors, connectors, dielectrics, shielding, contacts and so on and so forth. The materials and geometries through which the components are connected distinguish each cable from any other, bringing different improvements, nuances and colours. Provided the hi-fi system is revealing enough to bring all this to light. Each character that fills the stage dialogues with the other, interfering and aiming at a result that should be, by all, one: that of balance. In this regard, it may be useful to clarify the difference between diameter and cross-section in Hi-Fi cables.
Difference between conductor diameter and cross-section in Hi-Fi cables
All the components of a cable are important, especially if what connects the cable is equipment designed for high fidelity audio and video. Some of them, however, are really important, whether we are talking about a fine cable or Netzkabel of our washing machine. Let's think about the conductor. This is nothing more than the material that carries the electric current through the cable. So if it is true that every part is important, here we are dealing with one of the central elements.
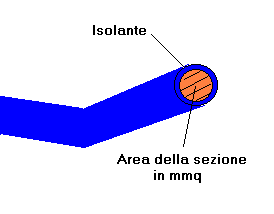
One of the most frequent uncertainties our customers have when consulting the technical specifications of a cable Ricable is the difference between the diameter and the cross-section of a cable. Let's start with one aspect: the first value is measured in millimetres, the second in square millimetres. The former is therefore a length, the latter an area. Let us now imagine that we are cutting any electrical cable and have it in front of us. We will see the conductor (or conductors) and, around it, the insulating material. The conductor, being cylindrical, will form a circle.
Well, the diameter of this circle is the diameter of the conductor, while the area of the circle is what is known as the cross-section of the conductor. The cross-section is therefore the area, expressed in square millimetres, formed by the copper wires passing through the insulating sheath. This value is particularly important as it is linked to the cable's ability to carry current or signal.
Why is cross-section used to measure conductors?
The question, at this point, is why is cross-section used to measure conductors and not diameter? The cross-section, constituting the area of the conductor, indicates the space in which there are copper wires passing through it. There are so many variables at this point: diameter of the strands, material of the strands, purity level of the copper, and still so much more. But in general we can say that a cable that has a large cross section will also be able to carry more current.
The question that might arise at this point is: why are strands referred to by diameter instead? The bad news is that the answer is not simple; the good news is that we already gave it to you a few articles ago-our most loyal customers will remember it. We refer to the skin effect, which we discussed in the article with which we inaugurated this blog. Those who want to go into it in more detail can do so by clicking on the article just linked. But to make a long story short, the argument is that the sound signal does not just pass inside strand. On the contrary, as a low-voltage electrical signal, it also and especially passes over the conductive surface of each individual strand. Reason why the diameter assumes primary importance. Also relevant, but in this case at installation, is the outer diameter of the entire cable, to see if we can run the same through conduit and furniture.
How is the diameter of a conductor calculated from the cross-sectional area?
If you want to calculate the diameter of a conductor from the cross-sectional area, a simple geometric formula will help you:
d = A / Π = √ = x2
Let's say we have a cross-section of 5 sq mm. To find the diameter, we need to divide this value by Pi (3.14). The result is 1.59. The square root of 1.59 is 1.26, which when multiplied by two becomes 2.52. The diameter of a conductor with a cross-section of 5 sq mm is 2.52 mm. On the Internet you can find tools that allow you to perform these and other calculations quickly, such as You Can Do!.

The importance of technical specifications in Hi-Fi cables
On every single product page of each cable Ricable you can find a comprehensive table to browse through, full of technical data such as capacity, strength, outer diameter, geometries and other characteristics. It is difficult for a cable manufacturer to provide so much detail to their customers, and the fact that many appreciate this transparency is particularly flattering to us. We hope that this article on the difference between diameter and cross-sectional area in Hi-Fi cables has been interesting and helpful. If you are curious to know all the cable numbers Ricable, we refer you to the full catalogue page!